Linux Mint is a popular Linux distribution known for its user-friendliness and elegance. One of the key components that contribute to its ease of use is the Linux Mint Update Manager. This tool is designed to keep your system up-to-date with the latest security patches, bug fixes, and software improvements.
What is the Linux Mint Update Manager?
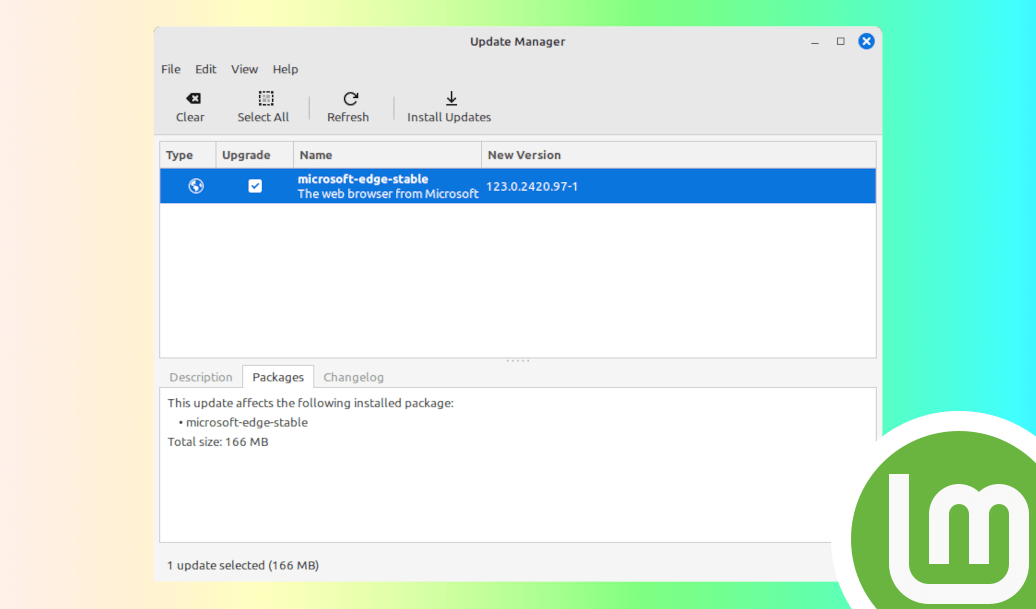
The Linux Mint Update Manager is a powerful graphical tool that simplifies the process of managing system updates. It notifies you when new updates are available and allows you to review and choose which updates to apply. The Update Manager categorizes updates based on their level of importance and potential impact on the system, helping users make informed decisions about what to install.
How Does the Linux Mint Update Manager Work?
When updates are available, the Update Manager displays a shield icon in the system tray. Clicking on this icon opens the Update Manager window, where you can see a list of available updates. By default, all updates are selected, but you can choose to deselect certain updates if you prefer.
Before applying updates, it’s recommended to create backups using Timeshift, a tool that comes pre-installed with Linux Mint. This precaution ensures that you can restore your system to a previous state if an update causes issues.
Differences Between Linux Mint and Other Distributions
While Linux Mint is based on Ubuntu and shares many similarities, there are several distinctions that set it apart:
- Update Philosophy: Linux Mint encourages users to apply all updates, but it also provides the flexibility to skip certain updates if desired. This approach contrasts with some other distributions that may apply updates automatically without user intervention.
- User Interface: Linux Mint offers a more traditional desktop experience with its Cinnamon desktop environment, which some users find more intuitive compared to the GNOME or KDE desktops commonly used in Ubuntu.
- Software Selection: Linux Mint comes with a variety of pre-installed software that is curated for immediate use, reducing the need for users to install additional software after the initial setup.
- Community vs. Commercial Support: Unlike distributions like Red Hat Enterprise Linux, which require a subscription for support and updates, Linux Mint is maintained by a community of volunteers and provides updates and support free of cost.
In conclusion, the Linux Mint Update Manager is a testament to the distribution’s commitment to providing a secure and user-friendly computing experience. Its thoughtful design and the distribution’s overall approach to updates, software selection, and community support make Linux Mint a compelling choice for both newcomers and seasoned Linux users alike.
For those interested in exploring the differences between Linux distributions further, there are resources available that explain in details the unique aspects of each, helping users choose the best fit for their needs. Whether you’re a desktop user, server administrator, or someone looking to revive an old machine, there’s a Linux distribution out there for you. Linux Mint is just one excellent example of the diversity and flexibility that Linux offers.